
5G and IoT revolutionize healthcare with real-time monitoring and remote procedures, breaking geographical barriers to quality care in underserved areas.

Drivetech Partners
The fusion of 5G technology with Internet of Things (IoT) is creating an unprecedented transformation in healthcare delivery models, especially in remote and underserved areas. This technological partnership provides the essential infrastructure for real-time monitoring, instantaneous data transmission, and remote procedures that were once considered impossible, effectively breaking down geographical barriers to quality healthcare.
Key Takeaways
Global 5G healthcare revenue is projected to reach $3.67 billion by 2026, driving exponential growth in remote care options
Ultra-low latency communication reaching 1 millisecond with 99.999% reliability enables critical applications like remote surgery
Over 60 million Americans used Remote Patient Monitoring in 2024, shifting healthcare from episodic to continuous care models
5G-enabled IoT wearables allow for real-time vital sign tracking without requiring in-person visits
Integration with AI and machine learning creates predictive healthcare models that can identify potential issues before they become critical
The Transformative Potential of 5G in Healthcare Delivery
The healthcare industry is experiencing a fundamental shift as 5G-enabled IoT devices reshape how care is delivered. This technological revolution goes far beyond simple connectivity improvements—it represents a complete reimagining of healthcare delivery models. The projected $3.67 billion in global 5G healthcare revenue by 2026 reflects the massive investment and growth in this sector.
Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM) has seen dramatic adoption rates, with more than 60 million people in the United States alone using these services in 2024. This surge is largely due to 5G's capacity to handle massive numbers of connected devices simultaneously while maintaining reliable performance.
5G's reduced capability (RedCap) technology serves as an important bridge between existing 4G LTE networks and full 5G implementation, ensuring the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) can evolve steadily without requiring complete infrastructure overhauls. This gradual transition path makes adoption more feasible for healthcare systems with budget constraints.

Breaking Barriers with Ultra-Low Latency Communication
The backbone of 5G's healthcare revolution is its Ultra-Reliable Low Latency Communication (URLLC) capability. This technology supports applications requiring 1 millisecond latency and 99.999% reliability—specifications that are critical for time-sensitive medical procedures where even minimal delays could have serious consequences.
Network slicing represents another breakthrough feature, allowing healthcare providers to create customized network connections tailored to specific medical needs. In emergency situations, this capability ensures that vital medical communications receive priority, potentially saving lives when networks are congested.
Edge computing capabilities further enhance 5G's healthcare applications by processing data closer to its source—whether that's a patient's wearable device or hospital equipment. This reduces critical response times and minimizes latency in scenarios where milliseconds matter, such as remote monitoring of unstable patients or guidance during emergency procedures.
Revolutionizing Telemedicine and Remote Diagnostics
The persistent connectivity issues that plagued earlier telemedicine efforts have been largely resolved through 5G implementation. Healthcare providers can now conduct high-definition video consultations while simultaneously receiving diagnostic data from connected devices—all in real-time.
A significant study by the Medical Device Innovation Consortium has confirmed that 5G accelerates remote healthcare delivery across multiple applications. The technology enables not just crystal-clear video consultations, but also real-time diagnostic reports and AI-driven medical insights that assist healthcare providers in making faster, more accurate diagnoses.
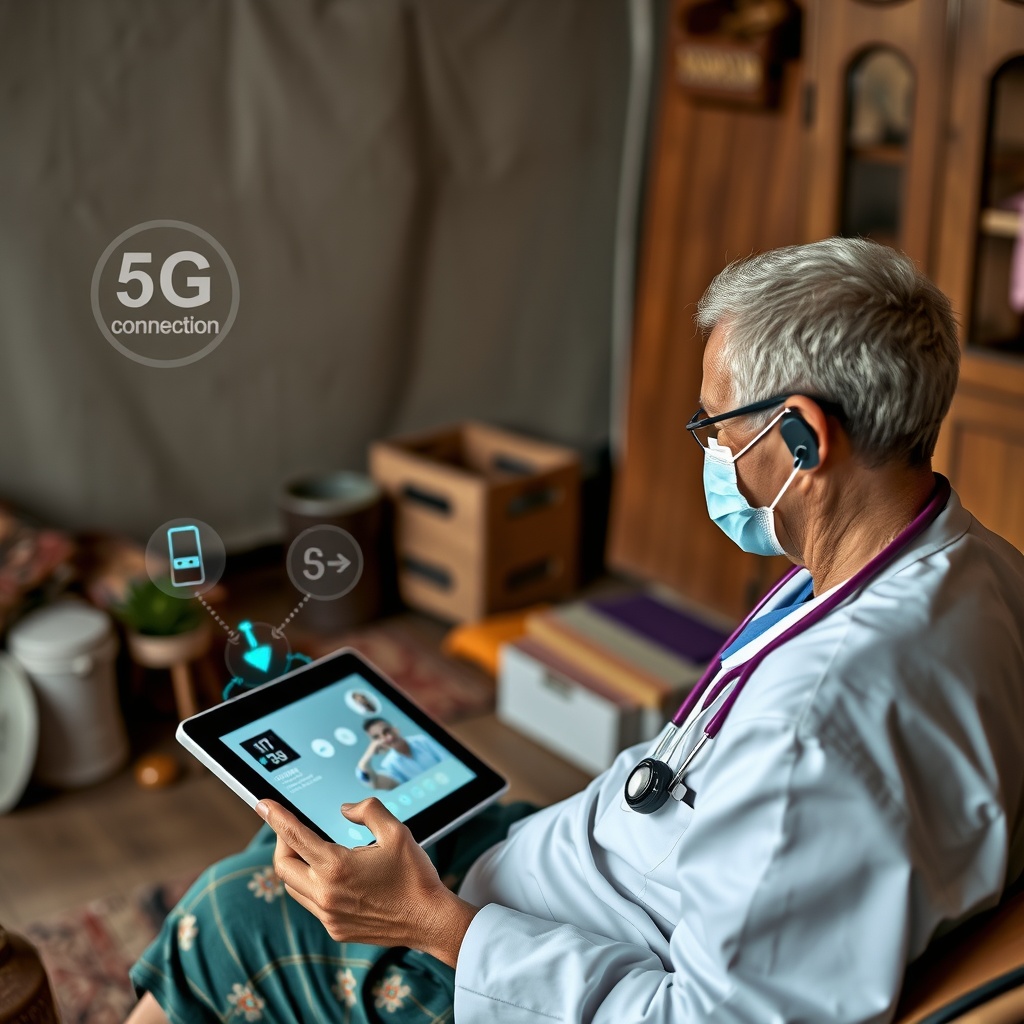

Perhaps most importantly, 5G-powered telemedicine expands access to specialized care in underserved and remote regions. Patients in rural areas who previously would have traveled hours for a specialist appointment can now receive expert care remotely, dramatically improving healthcare equity and outcomes in previously underserved communities.
The Connected Patient: IoT Wearables and Continuous Monitoring
IoT devices connected through 5G networks are transforming patient monitoring by tracking vital signs such as blood pressure, heart rate, oxygen levels, and glucose levels without requiring in-person visits. This represents a shift from episodic to continuous care models where healthcare providers have access to an ongoing stream of patient data.
The real-time nature of this data collection enables healthcare to become proactive rather than reactive. Instead of waiting for symptoms to become severe enough for a patient to seek care, providers can identify concerning trends in patient data and intervene earlier, often preventing complications or hospitalizations.
Wearable technology integration is particularly valuable for post-surgery monitoring, allowing for early detection of complications while patients recover at home. The combination of high-definition imaging from wearable or implanted devices with real-time data transmission creates a comprehensive remote monitoring system that rivals in-person observation for many applications.
Emergency Response Transformation with 5G
Emergency medical services have been revolutionized through 5G implementation, with enhanced communication between ambulances, hospitals, and paramedics. Smart ambulances now function as mobile treatment units, transmitting patient vitals and diagnostic information to emergency room teams while en route to the hospital.
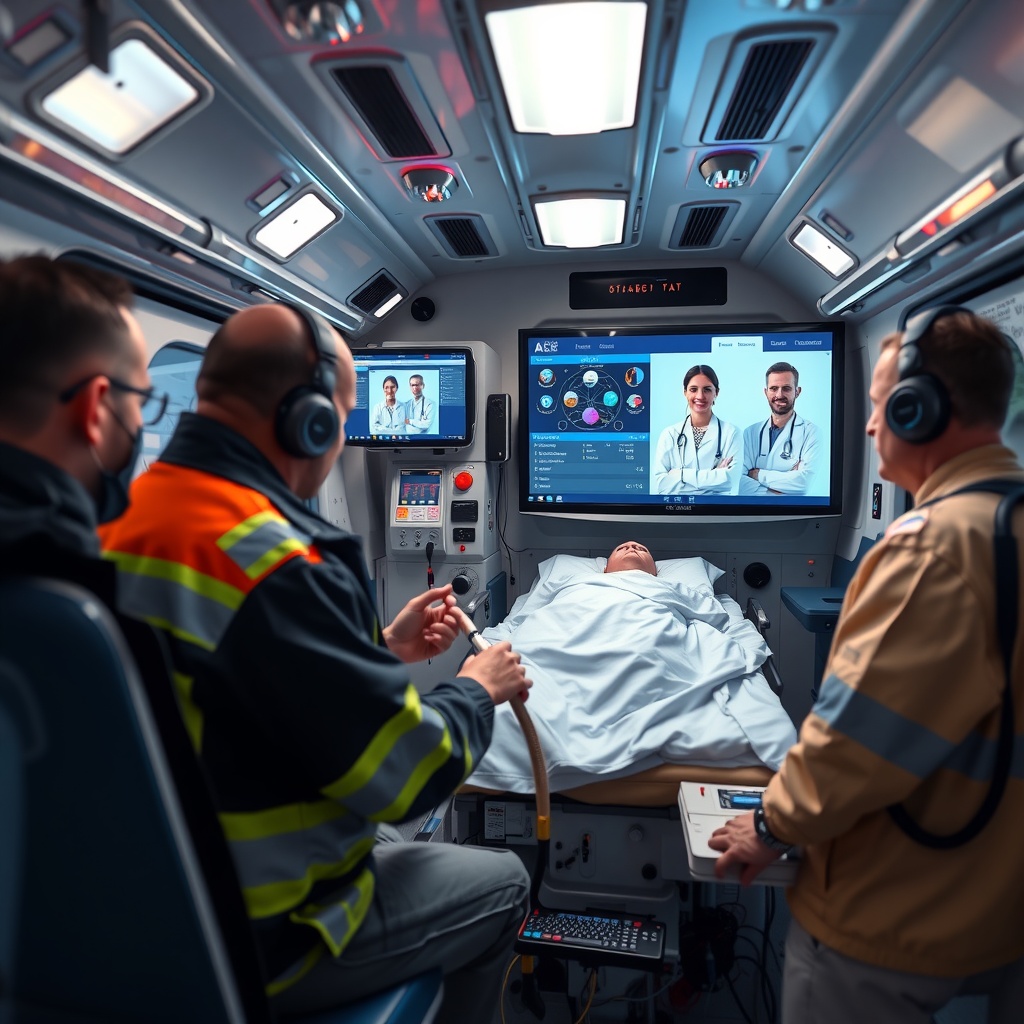

This capability allows emergency department staff to prepare appropriate resources before the patient arrives and enables paramedics to consult with specialists remotely via telehealth during transit. The high bandwidth and reliability of 5G ensures that critical information is transmitted successfully even in challenging network environments.
The net result is a significant reduction in critical response time and improved emergency outcomes. Treatment can effectively begin before the patient reaches the hospital, with specialized guidance available to first responders regardless of their location.
Remote Surgery and Advanced Medical Applications
Remote robotic surgery represents one of the most impressive applications of 5G in healthcare. This technology benefits from 5G's unique combination of low latency, high bandwidth, capacity, reliability, and security features—all essential for performing complex procedures remotely.
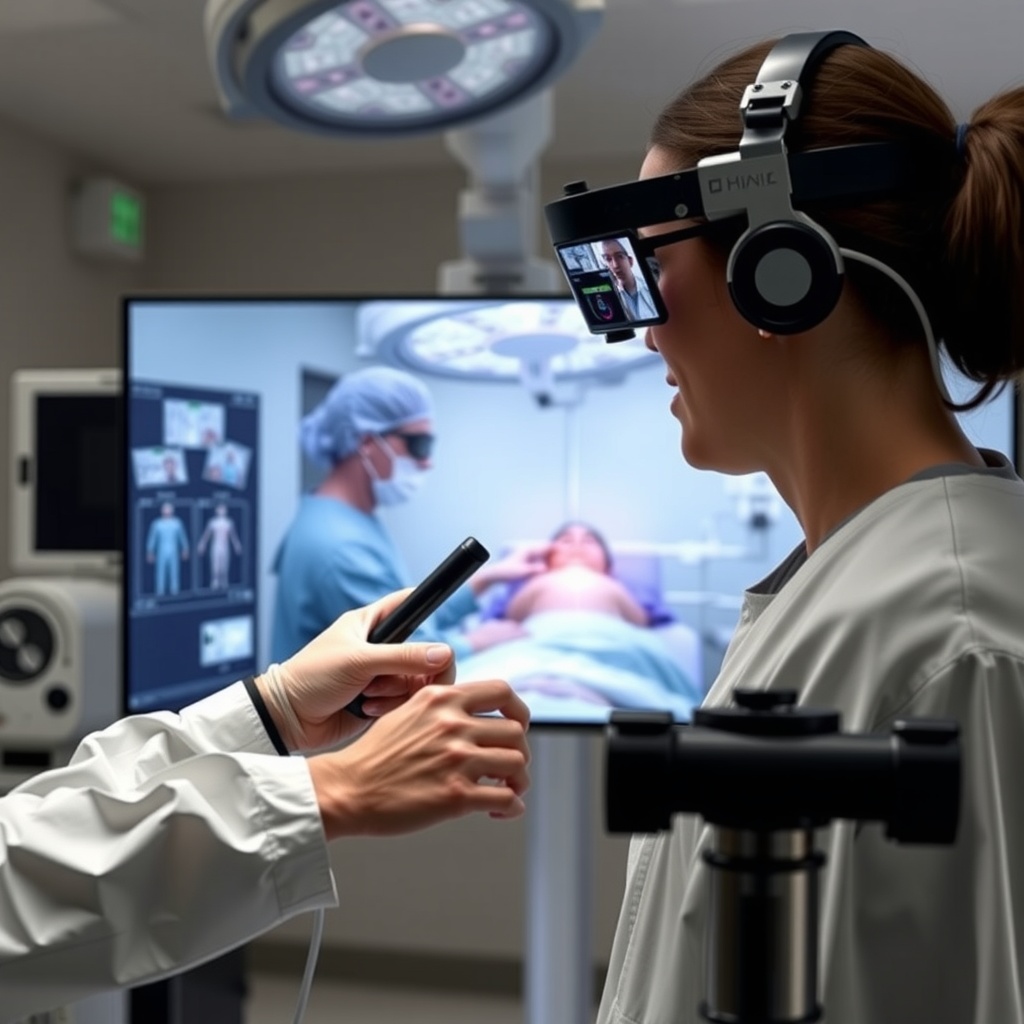
The integration of Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) with 5G infrastructure allows for innovative, less invasive treatments. Surgeons can visualize internal structures without making large incisions, and specialist surgeons can operate remotely, overcoming geographical barriers that previously limited access to specialized surgical care.
This technology also creates opportunities for surgical training and mentoring across vast distances. Experienced surgeons can guide less experienced colleagues through complex procedures in real-time, accelerating the spread of specialized surgical knowledge and improving outcomes in traditionally underserved areas.
AI and Machine Learning: The Data Intelligence Revolution
The massive connectivity capacity of 5G enables simultaneous connections to multiple IoT devices, generating unprecedented amounts of healthcare data for AI analysis. This data volume, combined with 5G's low latency, creates the perfect environment for advanced artificial intelligence applications in healthcare.
Integration of machine learning and AI with 5G multi-access edge computing (MEC) offers high levels of automation in healthcare settings. Healthcare providers increasingly have access to ML/AI-as-a-service offerings that can analyze complex patient data without requiring in-house AI expertise.
Perhaps most exciting is the emergence of AI-powered predictive analytics that can identify potential health issues before they become critical. By analyzing patterns across thousands of patients and billions of data points, these systems can detect subtle changes that might indicate developing problems, enabling truly preventive care approaches.
Challenges and Future Outlook
As 5G and IoT continue to transform healthcare, hospital-grade care is increasingly possible regardless of patient location. However, this rapid expansion brings important challenges that must be addressed for the technology to reach its full potential.
Data privacy and security concerns are paramount as healthcare IoT adoption grows. Robust cybersecurity frameworks are essential for maintaining patient trust and protecting sensitive medical information. The healthcare industry must develop comprehensive approaches to these challenges that balance innovation with appropriate safeguards.
Looking forward, the integration of 5G healthcare with other emerging technologies such as blockchain and quantum computing promises to further transform healthcare delivery. These combinations will likely create even more secure, efficient, and effective remote healthcare solutions while addressing current limitations.
Equitable access remains another significant challenge. As these technologies become more essential to quality healthcare, ensuring that all communities benefit from these advances—not just those in wealthy or urban areas—will be critical to preventing a new form of healthcare disparity.
Sources
Healthcare IT News - How IoT is transforming remote patient monitoring
Telit - 5G Connected Health Care Guide
Health Management - How IoT is transforming remote patient monitoring
Telit - 4 Revolutionary Use Cases 5G Healthcare
Times Tech - Healthcare Revolution: The Role of 5G-Enabled IoT in Transforming Care Delivery






